With the fast pace in today’s world, manufacturing industries have moved quickly towards digitalization. Yet, the path isn’t easy. The way is not however without twists and turns. It is important to outline and dissect these challenges of digital transformation in manufacturing for businesses that want to be more modernized.
Understanding Digital Transformation in Manufacturing
In manufacturing, digital transformation is the process of integrating digital technology into every aspect of business so as to alter fundamental working and value creation. This is not simply a technology shift, it is a mindset change that needs organizations to constantly question the norm, try new things and be comfortable with some that don’t work.
Why Digital Transformation Matters
In this day and age, going digital is not just a fancy option for manufacturing. We are living in a time of profound change, billed as the Third Industrial Revolution or ‘The Next Economy’. people want new stuff all the time and they want it their way. Therefore, if manufacturers won’t utilize digital tools, they’ll be left behind. Digital is not only about continuing – it’s about working in any area above and beyond; faster, more convenient to customer, fresh ideas.
- Increased Efficiency: Making things using digital tools is faster and cheaper.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Digital is about making things the way your customers want it.
- Innovation and Growth: Going digital enables you to think of new things to create and new ways in which you can make them.
Also Read: Role of Digital Transformation in Automotive Industry
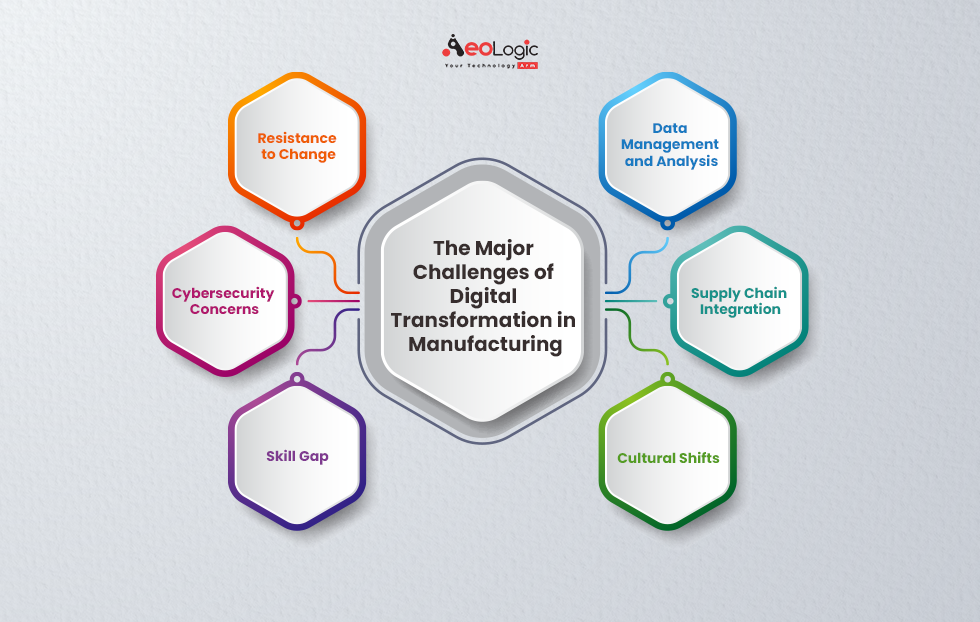
The Major Challenges of Digital Transformation in Manufacturing
Now let’s dive into the most significant barriers as manufacturers enter the digital world.
1. Resistance to Change
Resistance to change is one of the most important challenges of digital transformation in manufacturing. According to a McKinsey report, approximately 70 percent of change programs do not achieve their goals because of employee resistance and lack of managerial assistance. Such resistance naturally arises from fear of the unfamiliar as well as complacency. Employees might be afraid to lose their jobs or to be unable to adjust in time for new technologies.
Overcoming the Challenge:
Effective Communication: Therefore, all the advantages and need of digital transformation need to be clearly communicated. These changes should be able to make employees feel that they will benefit from them in the way they work and success of the company.
Inclusive Change Management: Resistance can be reduced if employees will be involved during change making. This may involve involving them in decision-making on new systems or creating avenues for them to air out their concerns and suggestions.
Training and Education: Offering elaborate training and education on the new digital tools makes the transfer easier while ensuring that workers are not job scared and suffer skill inadequacies.
Leadership Role: Change management calls for leadership. First they need to be the champions of the digital transformation, pathfinders, demonstrating their own involvement and enthusiasm in new technologies.
Gradual Implementation: The latter means that changes should not be introduced in digital matters abruptly. Instead, internal adjustments may be used to facilitate the transition and minimise resistance.
Manufacturers who address these facets, will succeed in containing resistance to change and therefore smoothen the road to a digitalized state.
Also Read: Digital Transformation Examples in Healthcare
2. Cybersecurity Concerns
Cybersecurity gains prominence as a major concern, thanks to manufacturers’ increasing adoption of the digital technologies. With digital networks being connected, they are at a great risk from many cyber threats, ranging from breaches of data to corporate espionage. According to Deloitte’s survey, 40% of the manufacturing companies were attacked last year with 38% losing an excess of $1 million.
The challenges here are multifaceted
- Protecting Intellectual Property: Cybercriminals target sensitive data such as patents and designs that are in control of the manufacturers.
- Securing the Supply Chain: Creating end-to-end security in the digital supply chain is difficult as it comprises of many different partners.
- IoT and Equipment Vulnerabilities: Nowadays manufacturing equipment is more connected, but also more vulnerable because of the growth of the Internet of Things (IoT). Ransomware Threats: Such attacks lock out manufacturers from their systems until payment of a ransom and can also halt production leading to financial losses.
Overcoming the Challenge
Tackling these issues requires a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy that includes:
- Regular Risk Assessments: Continuously assess and adjust security safeguards to address emerging threats.
- Employee Training: One common vulnerability is human error, which can be minimized through educating staff on cybersecurity best practices.
- Investing in Advanced Security Solutions: Deploy sophisticated security software and hardware to fight advanced attacks.
- Collaboration with IT Experts: collaborating with cyber security professionals to refine a strong defense strategy.
Manufacturers that address these cybersecurity concerns proactively can protect their digital transformation journey from the rising incidence of cyber attacks.
3. Skill Gap
There is a need for digital transformation for the work force with new technology competency. The problem is that it becomes difficult to find such a talent. The Manufacturing Institute and Deloitte report estimates the skill gap could result in up to 2.4 million job vacancies in manufacturing between 2018 and 2028.
Overcoming the Challenge
This gap can be bridged by offering training programs and partnering with academic bodies.
Also Read: Digital Transformation Examples in Marketing
4. Data Management and Analysis
For manufacturers, the stream of data from digital technologies is increasing in intensity. For one to make informed decisions, he or she must properly manage and analyze this much information, a thing that has proved hard for most of the people in the industry. This is especially the case when shifting from a conventional, labor-oriented operation to advanced, information-based operation.
In the age of big data, manufacturing companies are flooded with information from many different origins- equipment sensors, customer feedback, supply chain logistics among others. However, this data does not come without its struggle, but includes effective methods of organizing, storing and interpreting the same. However, this data is more of a liability than an asset when there are no adequate tools and expertise to deal with it.
Overcoming the Challenge
For manufacturers to turn this challenge into an opportunity, they must invest in strong data management. Such systems should be able to manage huge amounts of data and give unbeatable insights. In this regard, deciphering this data often involves hiring or training data analysts and scientists. Additionally, predictive analysis using technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) make data more useful in strategic planning.
5. Supply Chain Integration
Integrating digital technologies throughout the entire supply chain is one of the challenges that face digital transformation in manufacturing. This process is a delicate one as it involves numerous agents that possess individual systems and systems. Digital supply chain harmonization is key to sharing up-to-date data, bettering efficiency, and collaborating among suppliers, manufacturers, and distributers. It includes:
- Complex Interdependencies
- Visibility and Transparency
- Collaboration with Stakeholders
- Technological Hurdles
Overcoming the Challenge
To overcome these challenges, manufacturers need to:
- Build a full digital strategy, encompassing the whole supply chain.
- Align digital initiatives with supply chain partners.
- Choose scalable technologies that can operate in multiple systems and across multiple partners.
- Encourage transparency, promote data sharing within sensitive privacy boundaries.
- Train and support all stakeholders in changing to new processes of this digital problem.
End goal is to have a digital ecosystem where information is flowing freely, decisions are made with the support of data and the whole supply chain performs together in an efficient manner. The short response time to market changes and customer demands improves its operational efficiency.
Also Read: Top Digital Transformation Companies Leading the Way in 2023
6. Cultural Shifts
The push towards a digital-first manufacturing is more than technology change; it includes changing the culture of the organization. This is one of the underlying subtle and profound problems of digital transformation in manufacturing. It requires one to change the mindset from traditional ways of carrying out operations to more flexible and innovative methods.
Digital transformation culture captures the need for continuous learning, being flexible to adapt new ways of doing things, and trying out new technologies. Especially in work organizations with over two decades practising the tradition manufacture, this shift can be of challenge.
Overcoming the Challenge
Creating an environment that supports experiments and learning is crucial if the company is to succeed during this shift. Here, leadership is crucial. Leaders can also demonstrate the change by themselves which even might provoke other employees’ desire to get accustomed to new digital practices. Moreover, encouragement of employee’s proactive learning effort for new technology and rewarding feel can promote a foresighted culture.
This cultural shift is challenging initially, but it can create more dynamic competitiveness in the manufacturing environment. A culture of digital innovation enables a company to be responsive to changes in the market, improve efficiency, and support employees’ engagement and satisfaction.
Cultural dimension of digital transformation is as vital as technological component. Most importantly, a manufacturer can start to get over the biggest hurdle to digital ambitions a culture shift.
Final Words
Digital transformation in manufacturing is a challenging journey but not unbeatable. Through strategic planning, continual willingness to adapt, and emphasis on upskilling and cultural change, manufacturers can maneuver around these challenges back to success. Digital transformation should be looked as more than a tool for keeping up, but as a chance to reshapre manufacturing in the 21st century. Through such overcoming, the manufacturing sector can achieve levels of efficiency, innovation and growth here to unprecedented.
Navigate the Digital Transformation with Aeologic Technologies and Drive Manufacturing Success Into the Future.