Hello All, Today I’m here with another post to discuss another important aspect with respect to indexing operations in Solr. Invariably we encounter scenarios where we need to index data in a language of a different origin or more so, we need to index data of multiple languages. The dynamics to fulfil this requirement is of immense importance for any business given the gravity of the need. Solr helps to index the languages of different origins by having a language detection mechanism built for the same.
Essentially, Solr can identify languages and map text to language-specific fields during indexing using the langid UpdateRequestProcessor.
Solr supports three implementations of this feature:
- Tika’s language detection feature: https://tika.apache.org/1.17/detection.html
- LangDetect language detection: https://github.com/shuyo/language-detection
- OpenNLP language detection: http://opennlp.apache.org/docs/1.8.3/manual/opennlp.html#tools.langdetect
You can see a comparison between the Tika and LangDetect implementations here: http://blog.mikemccandless.com/2011/10/accuracy-and-performance-of-googles.html. In general, the LangDetect implementation supports more languages with higher performance.
Configuring Language Detection
You can configure the langid UpdateRequestProcessor in solrconfig.xml. Both implementations take the same parameters, which are described in the following section. At a minimum, you must specify the fields for language identification and a field for the resulting language code.
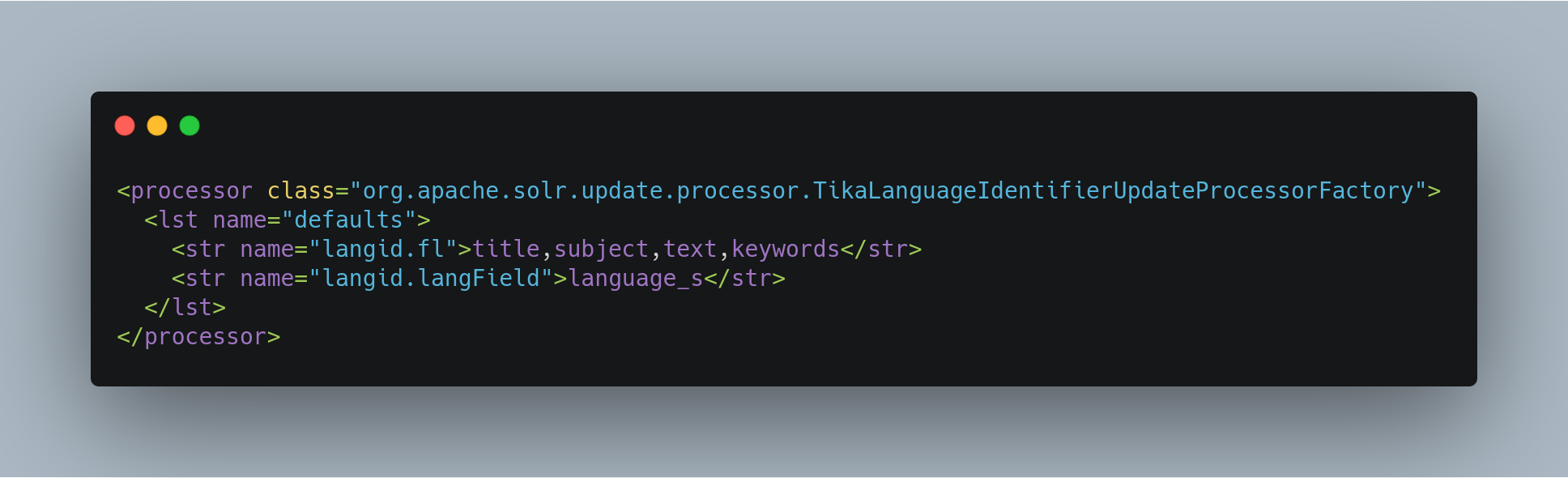
Configuring Tika Language Detection
Here is an example of a minimal Tika langid configuration in solrconfig.xml:
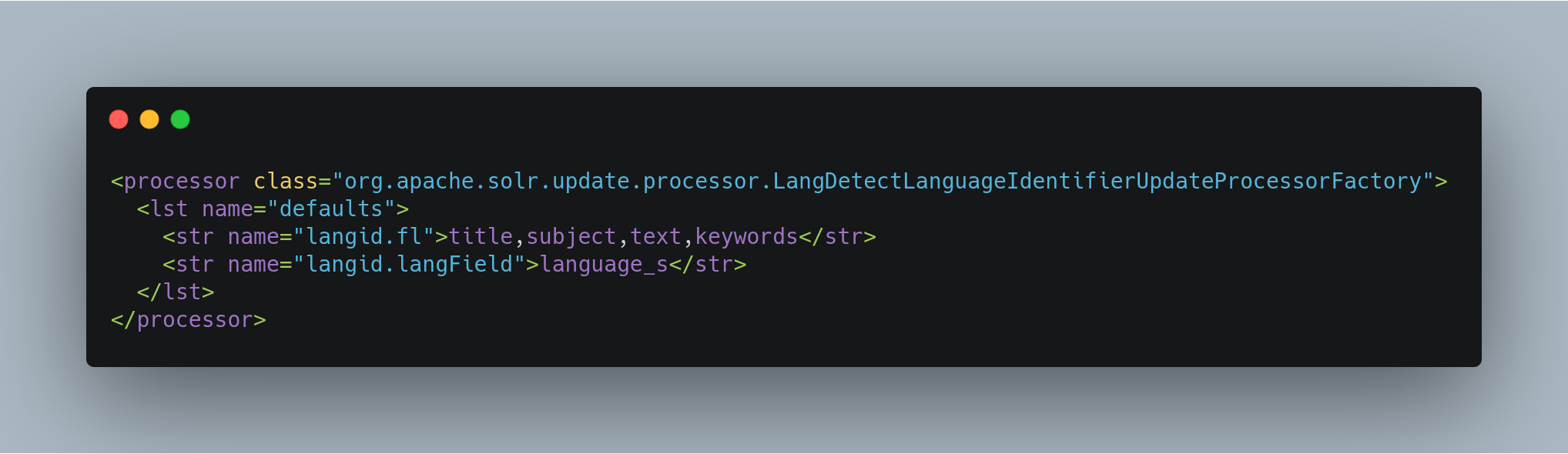
Configuring LangDetect Language Detection
Here is an example of a minimal LangDetect langid configuration in solrconfig.xml:
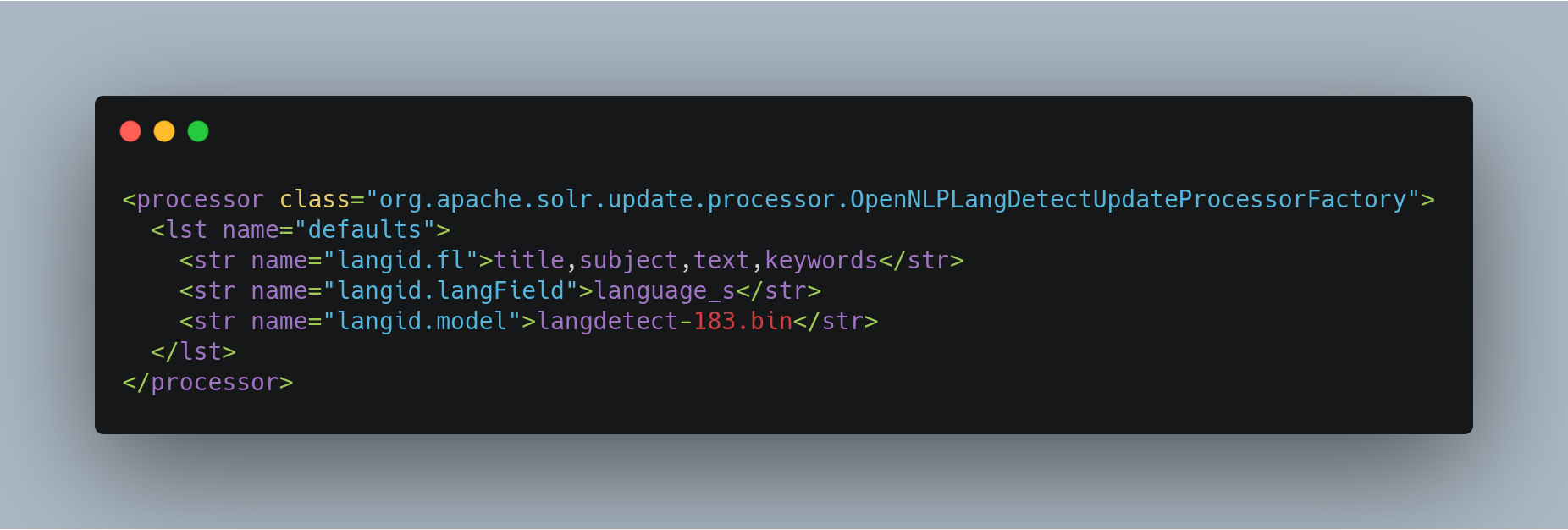
Configuring OpenNLP Language Detection
Here is an example of a minimal OpenNLP langid configuration in solrconfig.xml:
langid Parameters
As previously mentioned, both implementations of the langid UpdateRequestProcessor take the same parameters.
langid- When
true, the default, enables language detection. langid.fl- A comma- or space-delimited list of fields to be processed by
langid. This parameter is required. langid.langField- Specifies the field for the returned language code. This parameter is required.
langid.langsField- Specifies the field for a list of returned language codes. If you use
langid.map.individual, each detected language will be added to this field. langid.overwrite- Specifies whether the content of the
langFieldandlangsFieldfields will be overwritten if they already contain values. The default isfalse. langid.lcmap- A space-separated list specifying colon delimited language code mappings to apply to the detected languages.
For example, you might use this to map Chinese, Japanese, and Korean to a common
cjkcode, and map both American and British English to a singleencode by usinglangid.lcmap=ja:cjk zh:cjk ko:cjk en_GB:en en_US:en.This affects both the values put into the
langFieldandlangsFieldfields, as well as the field suffixes when usinglangid.map, unless overridden bylangid.map.lcmap. langid.threshold- Specifies a threshold value between 0 and 1 that the language identification score must reach before
langidaccepts it.With longer text fields, a high threshold such as
0.8will give good results. For shorter text fields, you may need to lower the threshold for language identification, though you will be risking somewhat lower quality results. We recommend experimenting with your data to tune your results.The default is
0.5. langid.whitelist- Specifies a list of allowed language identification codes. Use this in combination with
langid.mapto ensure that you only index documents into fields that are in your schema. langid.map- Enables field name mapping. If
true, Solr will map field names for all fields listed inlangid.fl. The default isfalse. langid.map.fl- A comma-separated list of fields for
langid.mapthat is different than the fields specified inlangid.fl. langid.map.keepOrig- If
true, Solr will copy the field during the field name mapping process, leaving the original field in place. The default isfalse. langid.map.individual- If
true, Solr will detect and map languages for each field individually. The default isfalse. langid.map.individual.fl- A comma-separated list of fields for use with
langid.map.individualthat is different than the fields specified inlangid.fl. langid.fallback- Specifies a language code to use if no language is detected or specified in
langid.fallbackFields. langid.fallbackFields- If no language is detected that meets the
langid.thresholdscore, or if the detected language is not on thelangid.whitelist, this field specifies language codes to be used as fallback values.If no appropriate fallback languages are found, Solr will use the language code specified in
langid.fallback. langid.map.lcmap- A space-separated list specifying colon-delimited language code mappings to use when mapping field names.
For example, you might use this to make Chinese, Japanese, and Korean language fields use a common
*_cjksuffix, and map both American and British English fields to a single*_enby usinglangid.map.lcmap=ja:cjk zh:cjk ko:cjk en_GB:en en_US:en.A list defined with this parameter will override any configuration set with
langid.lcmap. langid.map.pattern- By default, fields are mapped as <field>_<language>. To change this pattern, you can specify a Java regular expression in this parameter.
langid.map.replace- By default, fields are mapped as
<field>_<language>. To change this pattern, you can specify a Java replace in this parameter. langid.enforceSchema- If
false, thelangidprocessor does not validate field names against your schema. This may be useful if you plan to rename or delete fields later in the UpdateChain.The default is
true.
So, this is it on language detection in Solr. Stay tuned for another post about “Language Analysis” in Solr.





