When you pick up a product, be it a toy, a gadget, or even food, have you ever wondered about its journey? From the raw materials to its final form, the process of manufacturing is complex. And one key element that ensures this process runs smoothly and safely is traceability. In this article, we’ll dive into the significance of traceability in the world of manufacturing and why it’s become an essential component of modern industry practices.
What is Traceability?
Before we delve deeper, it’s essential to understand what traceability is. Traceability is the capability to trace (or track) every step in the lifecycle of a product. This includes its origin, production, distribution, and even its disposal. Now, you might wonder, why is this so crucial. The answer lies in the importance of traceability in manufacturing.
Do you know? Role of Traceability in Sustainable Supply Chain Management
What is Traceability in Manufacturing?

Traceability in manufacturing refers to the systematic ability to track and trace the journey of a product or component throughout its entire production and distribution process. It’s like a product’s biography, providing insights into its origin, the materials used, the processes it underwent, and where it eventually ends up. Understanding this journey is pivotal, emphasizing the importance of traceability in manufacturing in ensuring quality, safety, and compliance.
Also Read: What is Traceability and Its Challenges in Industry
How Does Traceability Work in Manufacturing?
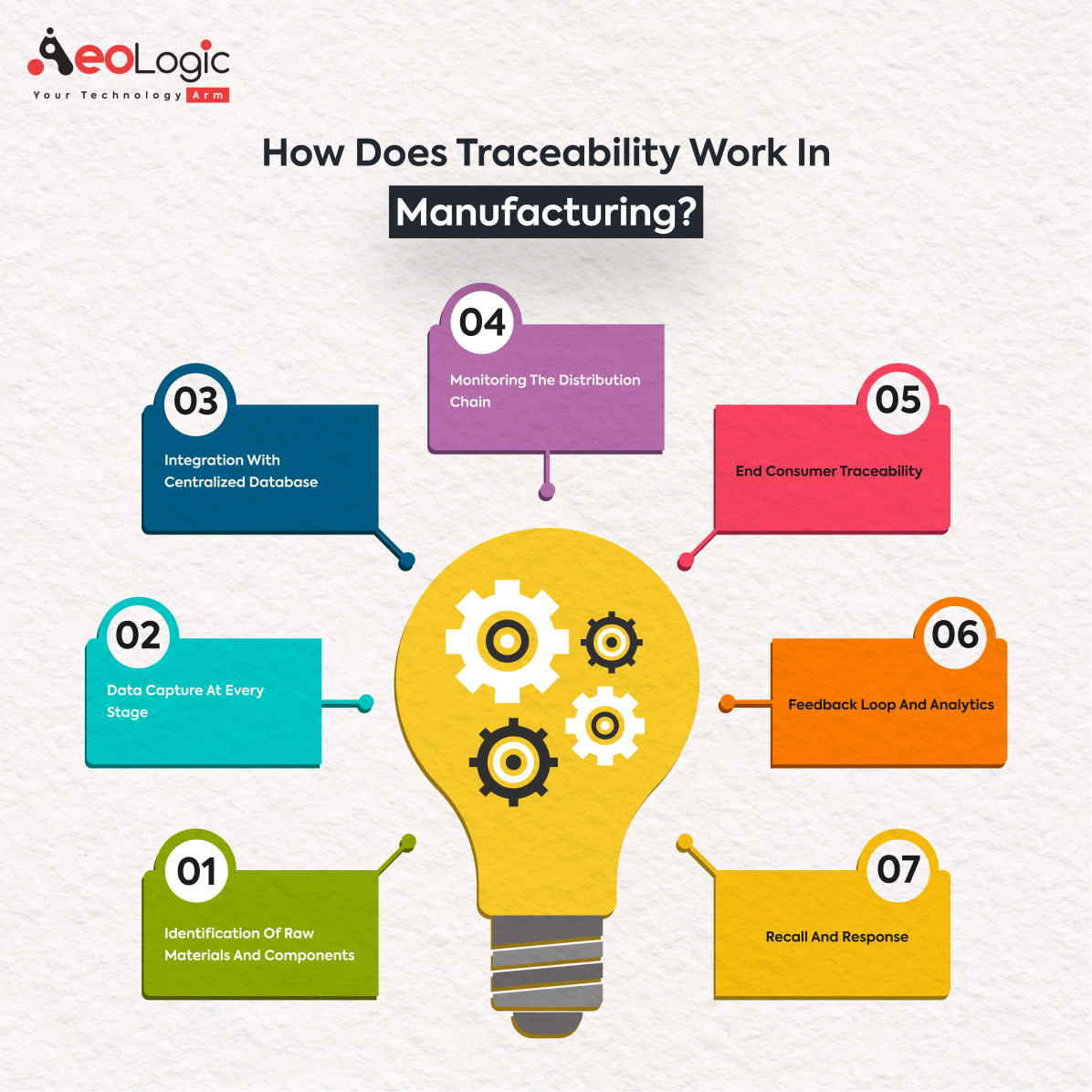
Traceability in manufacturing is not a mere concept but a structured process. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how it typically works:
Step 1. Identification of Raw Materials and Components
Every raw material or component entering the manufacturing facility is tagged with a unique identifier, typically through barcodes, QR codes, or RFID tags.
Step 2. Data Capture at Every Stage
As the product moves through various stages of manufacturing, data is captured. This can include information about the machinery used, operators involved, time spent, and any quality checks performed.
Step 3. Integration with Centralized Database
All the captured data gets integrated into a centralized database. This allows for real-time monitoring and ensures that every detail about the product is stored and easily retrievable.
Step 4. Monitoring the Distribution Chain
Once the product is ready for distribution, its journey doesn’t end. Traceability continues as the product moves through the supply chain, from warehouses to distributors to retailers.
Step 5. End Consumer Traceability
With advanced traceability systems, even consumers can access information about the product. By scanning a code on the product, they can get insights into its origin, production details, and more.
Step 6. Feedback Loop and Analytics
The data collected isn’t just for tracking; it’s also used for analytics. Manufacturers can analyze this data to identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, or areas of improvement in the production process.
Step 7. Recall and Response
If a defect or issue is identified in a batch of products, the traceability system allows manufacturers to pinpoint the exact batch or even specific items affected. This makes recalls more efficient and ensures that faulty products are removed from the market swiftly.
Also Read our trending blog: Traceability Solutions for Supply Chains with Examples
Top Reasons Why Traceability is Essential in Manufacturing

Manufacturing is a multifaceted domain, and as complexities grow, the “importance of traceability in manufacturing” becomes more pronounced. Here are seven key reasons, each supplemented with a relevant example, showcasing why traceability is indispensable in modern manufacturing:
1. Ensuring Product Safety
In the battle against counterfeit products, traceability is the frontline defense. By allowing manufacturers to verify a product’s authenticity, consumers are assured they’re receiving genuine items. Moreover, if a product fault emerges, traceability facilitates efficient recalls, targeting only the affected batches, thus minimizing disruptions.
Example: In 2007, Mattel recalled millions of toys due to concerns over lead paint. Traceability systems enabled them to identify and recall only the affected products swiftly.
2. Meeting Regulatory Standards
As products weave their way through global markets, they encounter varied regulatory landscapes. Traceability ensures that from production to final delivery, every product complies with the multifarious international standards it must navigate, safeguarding both manufacturers and consumers.
Example: In the pharmaceutical industry, stringent regulations like the Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA) in the U.S. necessitate traceability to track prescription drugs through their distribution journey.
3. Boosting Consumer Confidence
Today’s consumers crave more than just quality; they seek transparency. Traceability provides a clear view of a product’s journey, from its origins to its final form. This transparency builds a robust foundation of trust between consumers and brands, fostering loyalty and assurance.
Example: Brands like Patagonia provide QR codes on their garments, allowing consumers to trace the journey of the clothing item from raw material to finished product.
4. Enhancing Operational Efficiency
Efficiency is the lifeblood of manufacturing. With traceability, every step of the production process is under scrutiny, enabling manufacturers to identify and rectify inefficiencies swiftly. Moreover, by optimizing resource allocation, wastage diminishes, leading to a leaner, more profitable operation.
Example: Automotive giants like Toyota employ traceability in their production lines to identify bottlenecks or defects quickly, ensuring a streamlined manufacturing process.
5. Risk Management
The unpredictable nature of manufacturing means that risks are ever-present. Whether it’s a product fault or a supply chain hiccup, traceability equips manufacturers with the data they need for rapid assessment. This swift response can mitigate potential fallout, be it financial, reputational, or operational.
Example: In 2018, a major cereal brand faced an outbreak of salmonella linked to its products. With traceability, the brand could quickly identify and isolate the affected batches, preventing further spread.
6. Supply Chain Transparency
A transparent supply chain is a resilient one. By pinpointing the origins of each component, traceability ensures that suppliers maintain the highest standards of quality and ethics. This not only guarantees product integrity but also fortifies the entire production ecosystem against potential vulnerabilities.
Example: Companies like Starbucks employ traceability to ensure their coffee beans are sourced ethically and sustainably, offering consumers insights into the beans’ origins and the farmers behind them.
7. Competitive Advantage
In the fiercely competitive world of manufacturing, differentiation is crucial. A robust traceability system not only underscores a commitment to quality but also signals a dedication to transparency and consumer trust. In a market where discerning consumers value these attributes, traceability can be the edge that sets a brand apart.
Example: Luxury brands, such as Louis Vuitton, use traceability to authenticate their products, providing consumers with assurance of genuine products and setting themselves apart in a market rife with replicas.
In essence, the importance of traceability in manufacturing is not just a buzzword; it’s the cornerstone of modern manufacturing, ensuring quality, trust, and resilience in an ever-evolving landscape.
Also Read: The Role of Traceability in the Textile Industry
The Future of Traceability in Manufacturing
In a rapidly evolving world where technology permeates almost every aspect of our lives, the manufacturing sector is no exception. As we’ve discussed the importance of traceability in manufacturing, it’s crucial to delve deeper into what the future holds for this critical aspect of the production process.
1. Integration of Advanced Technologies
The realm of traceability is continuously being reshaped by cutting-edge technologies. These technologies not only make traceability more precise but also adapt to the dynamic needs of modern manufacturing.
- Blockchain: A decentralized technology ensuring product authenticity and transparency.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: These tools offer predictive analysis and optimize the traceability process.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices, such as sensors, provide real-time data and enhance the immediacy of traceability.
- RFID (Radio Frequency Identification): This technology uses electromagnetic fields to identify and track tags attached to objects, offering real-time data.
- Barcodes: A traditional yet indispensable tool for traceability, offering simplicity and widespread acceptance.
2. Greater Emphasis on Sustainability
With increasing global emphasis on sustainability, the “importance of traceability in manufacturing” will also encompass tracking the environmental impact of products. This includes the carbon footprint of raw materials, water usage, and waste generated. Such traceability ensures that manufacturers adhere to sustainable practices, leading to greener products and processes.
3. Consumer-Driven Traceability
The modern consumer is well-informed and often demands transparency. In the future, consumers will play a more significant role in driving traceability. There will be an increased demand for apps and platforms that allow consumers to scan products and access detailed information about their origins, production processes, and more.
4. Global Standardization
As global markets become more interconnected, there will be a push towards standardized traceability protocols. This ensures that products, no matter where they are manufactured or sold, adhere to a consistent set of traceability standards, simplifying international trade and ensuring product quality.
5. Enhanced Collaboration
Future traceability will not be limited to individual manufacturers. There will be increased collaboration between suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and even consumers. Shared platforms and systems will allow for a more holistic view of a product’s journey, from raw material to end consumer.
Final Words
The importance of traceability in manufacturing cannot be stressed enough. It’s the backbone of safe, efficient, and trustworthy production processes in today’s interconnected global market. As consumers become more discerning and regulations become stricter, the role of traceability will only grow, making it a pivotal aspect of modern manufacturing.
So, the next time you pick up a product, take a moment to appreciate the intricate journey it’s been through and the systems in place that ensure its quality and authenticity. After all, it’s not just about the end product; it’s about the journey it takes to get there.
Every step of the way, Aeologic Technologies is there, making sure things are done right and products can be trusted.






