In today’s tech world, data is everywhere. From factories to hospitals and even retail stores, businesses are collecting more data than ever before. But what good is all this data if it can’t be processed quickly? This is where Edge Computing steps in. Unlike traditional cloud computing, where data travels back and forth to distant servers, Edge Computing brings the processing power closer to where the data is created. The global edge computing market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 19% from USD 36.5 billion in 2021 to USD 87.3 billion by 2026. This explosive growth highlights the critical role Edge Computing in Real-Time Data Processing plays in industries worldwide.
What is Edge Computing?
In simple terms, Edge Computing is all about processing data. Where it’s generated—at the “edge” of the network, rather than sending it to a cloud server. This cuts down on the time it takes to make decisions allowing businesses to respond faster. Imagine an automated assembly line if a machine senses a defect it needs to react immediately. With Edge Computing, the data doesn’t have to travel far, enabling instant action.
Also Read: Top Benefits of Implementing Edge Analytics for IoT Devices
Why Real-Time Data Processing Matters
In industries like healthcare, manufacturing, and retail, every second counts. Real-time data means decisions can be made instantly. For instance, in the medical field, real-time patient monitoring can save lives by alerting doctors to changes in a patient’s condition without delay.
Edge Computing makes this possible by processing data locally. It reduces the lag time, or latency, between data creation and response. It helps industries make faster decisions by processing data instantly.
Also Read: The Benefits of Edge Computing for Businesses
Key Sectors Benefiting from Edge Computing in Real-Time Data Processing
Here’s a closer look at how it’s reshaping industries:
Manufacturing
Edge Computing plays a vital role in smart factories. Here machines, robots, and systems need to operate seamlessly. By processing data locally, Edge Computing enables real-time monitoring of equipment. This kind of predictive maintenance prevents downtime and costly repairs. For instance, a sensor on a production machine can detect unusual vibrations or temperatures. It helps make quick fixes. This prevents defects and keeps things on time.
Healthcare
In healthcare real-time patient monitoring can be the difference between life and death. Edge Computing helps hospitals and clinics analyze data from medical devices. This technology is especially valuable in critical care settings. Any delay could impact patient outcomes. For example, wearable devices that track heart rates, oxygen levels, and blood pressure can alert healthcare providers instantly. If a patient’s condition changes. Edge Computing ensures that data from these devices is processed quickly and securely.
Retail
The retail industry uses Edge Computing to understand customer behavior and streamline operations in real time. For example smart shelves equipped with sensors can track inventory levels and send alerts when stock is low.
It enables personalized shopping experiences by analyzing customer data. It can help retailers quickly adjust in-store advertising based on what’s trending. By ensuring that promotions resonate with customers’ current interests.
Transportation and Logistics
Edge Computing provides real-time insights that reduce costs. Fleet management systems use sensors and GPS data processed. To monitor vehicle locations fuel consumption, and driving behaviors. This information is critical for optimizing routes, reducing fuel costs, and ensuring timely deliveries.
In public transportation it enables real-time monitoring of vehicle conditions. It allows operators to manage schedules better and improve safety. For example, logistics companies can reroute trucks immediately if there’s an accident on a primary delivery route, preventing delays and minimizing costs.
Agriculture
Precision agriculture relies on data from sensors placed throughout the fields. Edge Computing allows these sensors to process data on soil moisture, temperature, and nutrient levels in real time. By analyzing this data locally farmers can make immediate adjustments to irrigation or fertilization.
This approach saves resources and enhances crop yield. The right amount of water and nutrients at the right time. In livestock farming, edge devices monitor animal health, if conditions like temperature or movement patterns change.
Energy and Utilities
The energy sector benefits significantly from Edge Computing by monitoring power grid performance in real-time. Smart grids can detect power outages, manage electricity flow, and optimize energy distribution instantly.
For renewable energy, Edge Computing helps in monitoring conditions like wind speed, solar radiation, and turbine efficiency. It allows companies to optimize energy generation. This is especially crucial as the demand for renewable energy rises.
Financial Services
Edge Computing enhances fraud detection and risk management in financial services. For instance, when an unusual transaction occurs, edge-based systems can immediately flag it.
Financial institutions also use Edge Computing to process large volumes of financial data, ensuring quick responses in a highly dynamic market. Real-time trading platforms rely on edge technology to execute trades at lightning speed.
Smart Cities
Edge Computing enables cities to manage traffic flow. Traffic cameras and sensors installed at intersections can process data locally. It allows cities to adjust traffic signals instantly based on congestion levels.
Public safety is also enhanced by processing data from surveillance cameras. Edge Computing also helps smart cities manage lighting, waste, and energy, creating a more sustainable urban environment.
Related Blog: The Role of Edge Computing in IoT Applications
Advantages of Edge Computing in Real-Time Data Processing
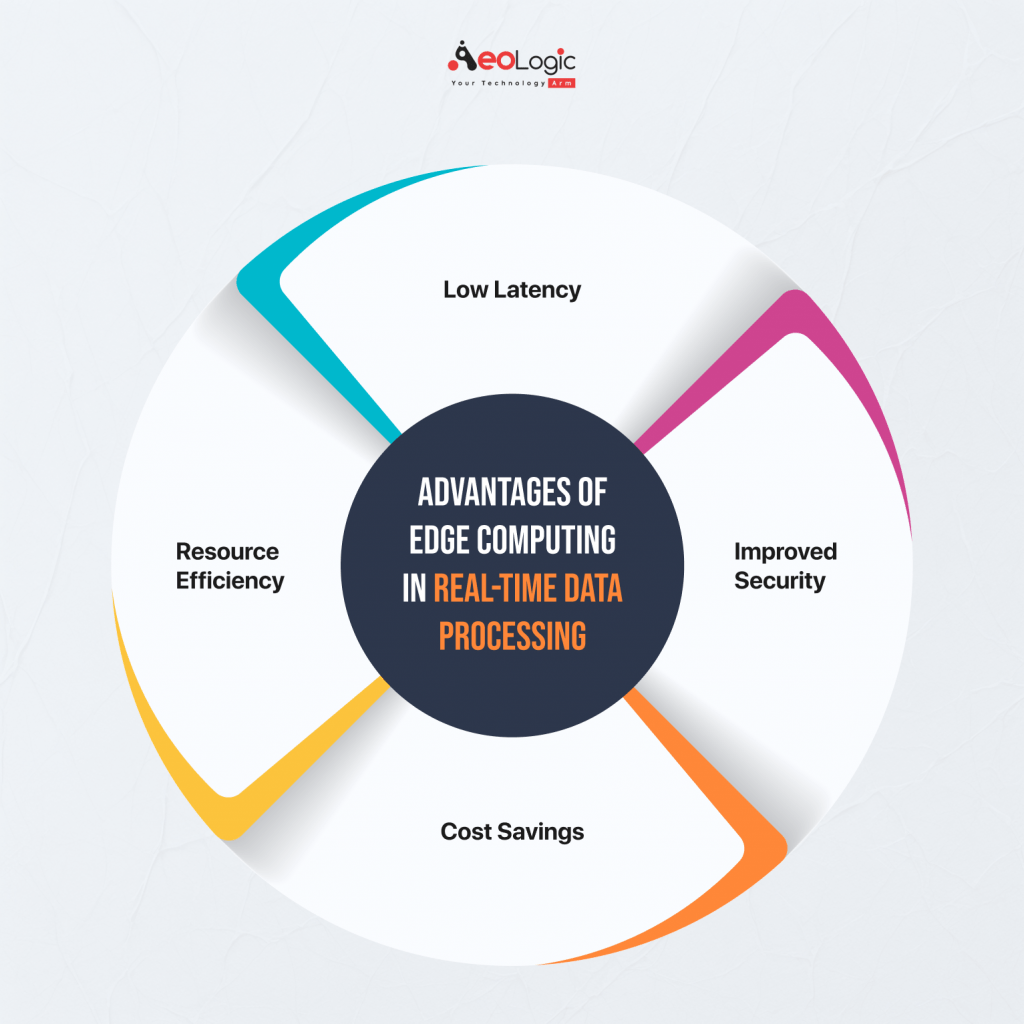
Edge Computing brings many benefits, making it essential for businesses focused on efficiency:
- Low Latency: By processing data locally, Edge Computing reduces response times, which is crucial for time-sensitive tasks.
- Improved Security: Sensitive data stays closer to its source, reducing the risks that come with sending it to a central server.
- Cost Savings: Since less data is transmitted to the cloud, bandwidth costs drop, and systems don’t rely as heavily on internet connections.
- Resource Efficiency: Edge Computing can handle tasks independently, optimizing system resources.
Also Read: Edge Computing is Shaping the Future of Business
Final Words
Edge Computing in Real-Time Data Processing is transforming the way we handle data. By keeping data processing closer to the source, we see faster response times. If a business wants to succeed today, it needs Edge Computing. This technology helps handle data faster. It’s not just a choice anymore; it’s essential.